In February 2022, I signed up for Ivan Zamesin’s course on product development. This post is a collection of my notes from the lectures.

Lecture 1. Why Do People Buy or Do Anything
People make decisions in this way:
- first an emotion,
- then a decision,
- and finally rationalisation.
People’s need can be unconscious, partially conscious and fully conscious.
It’s almost impossible to discover unconscious needs. Other types can be discovered by the interviews.
The task of the product is to understand what pleasant and unpleasant emotions people feel in the situation in question, and then offer a way to reduce unpleasant emotions and increase the number of pleasant ones through the product.
The algorithm for detecting emotions:
- Ask about the situation — The courier was late, I stayed hungry.
- What’s bad about the courier being late and you staying hungry? — Things didn’t go according to plan! (What was the plan?) — I was planning to finish the call and eat, and now I’ve to wait even longer. I felt upset and annoyed.
- Ok. So you were upset and annoyed, right? — Yes
- If 10 is the greatest annoyance in the world, how angry were you? — Like 4.
- How often do you find yourself in this situations like the one you described?
Estimating the strength of an emotion is only necessary to compare problems with each other. In addition to strength, it’s also important to assess frequency.
Common negative emotions: fear, anger, guilt.
Lecture 2. Intro into Jobs to be Done Framework
How people act
- A person is in a certain context and in some emotional state and wants to arrive to some other emotional state.
- A person «formulates» a mental request to the brain «please make it so I would arrive to some this emotional state».
- A brain tries to guess the best solution.
Definition of the Job
A job is the abstraction on top of aforementioned algorithm:
- When… (mindset, context, trigger)
- I want… (a clear result)
- So that… (new emotional state)
- Solution… (what do clients hire)
- Problems with this solution (a problem may exist only in the context of a solution)
A Hierarchy of Jobs
Since each person has different needs, all possible jobs are placed in a hierarchy.
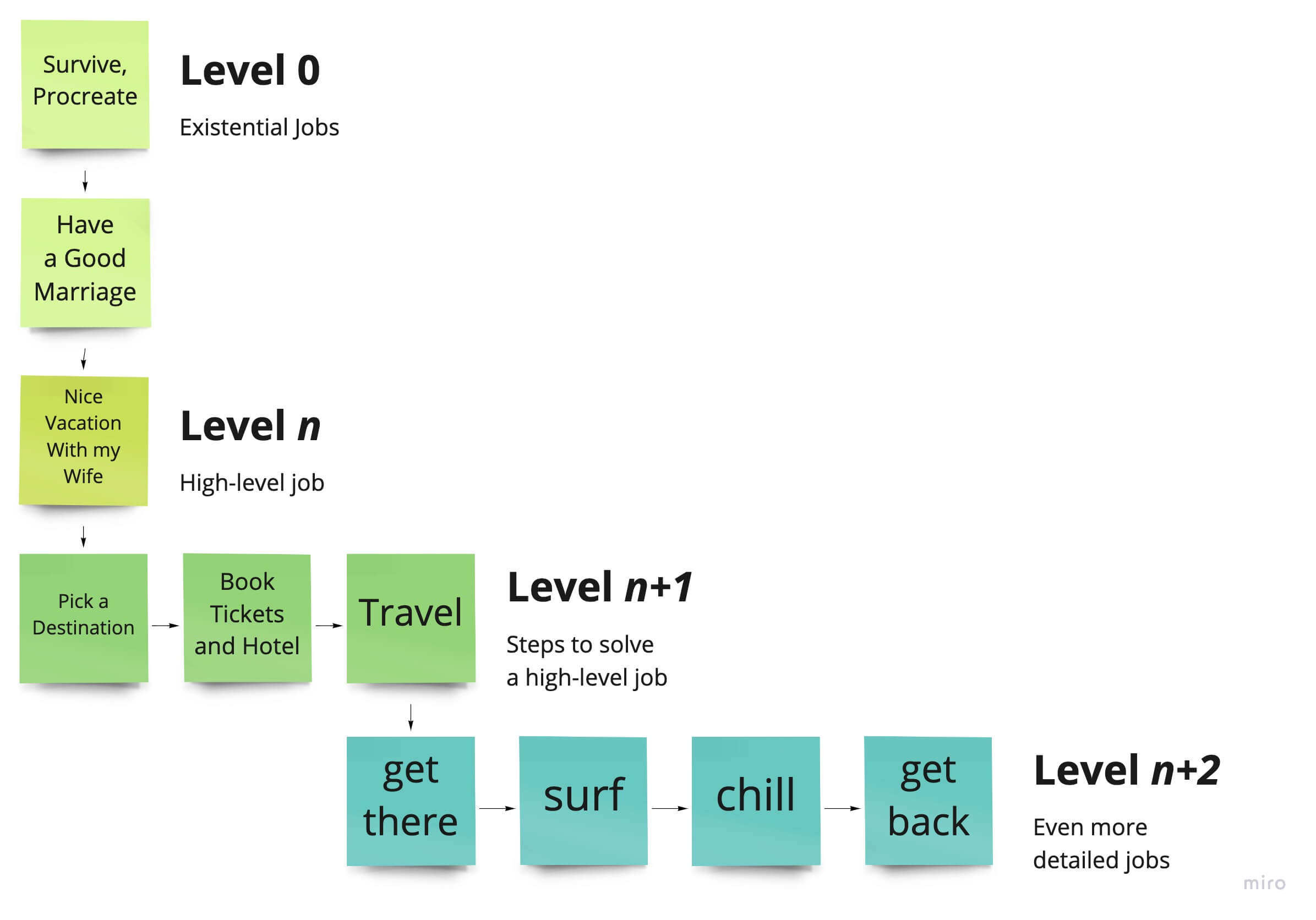
Each job is placed somewhere on the hierarchy
For example, on the existential level, I want to survive and procreate. So I want to have a happy marriage.
A marriage is happier when we’re well rested, so I want to go on a nice vacation with my wife. To go on a vacation, I need to choose a destination, buy tickets and book a hotel, and then we’ve to go.
During the trip, we’ve to arrive at our destination, get settled in the hotel, have dinner, rest, then go surfing, party and chill. And when the vacation is over, we’ve to go home again.
Job Types
JTBD Interviews
There are a variety of different JTBD interviews. Right now we are focusing on two: segment search and product search.
Segment Search
 Segment Search Interview Template
Segment Search Interview Template
In the Segment Search interviews, the interviewer asks about how people have solved a series of
Product Search
The Product Search Interview is very similar to the Segment Search Interview, but it focuses on a single selected segment and on examining a series of specific steps that people take to accomplish a job. For example, «How do you usually book hotels?».